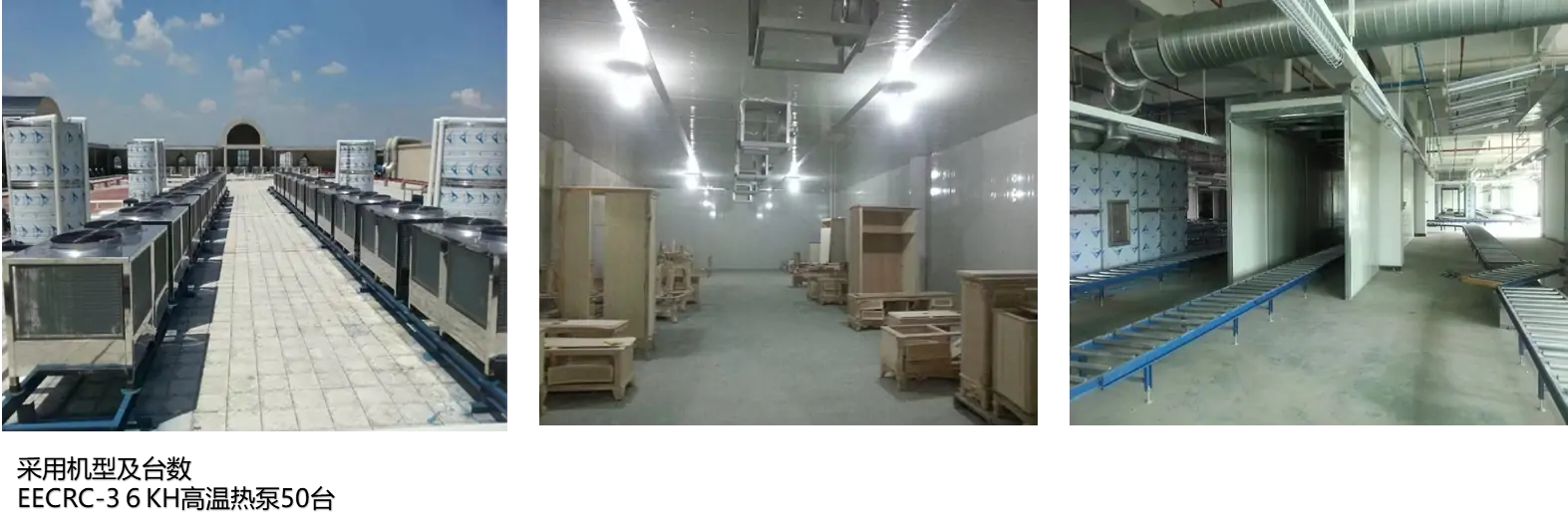
Civilian Water cooling unit Solution systems
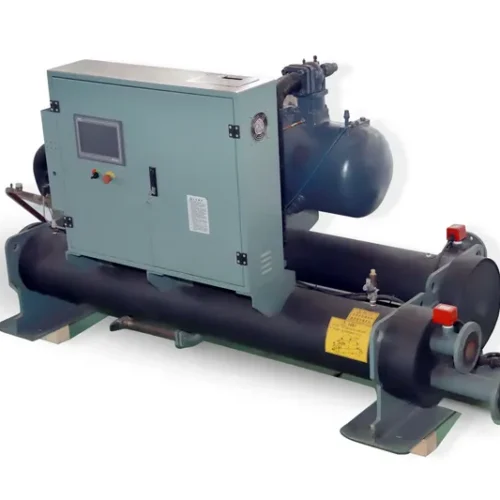
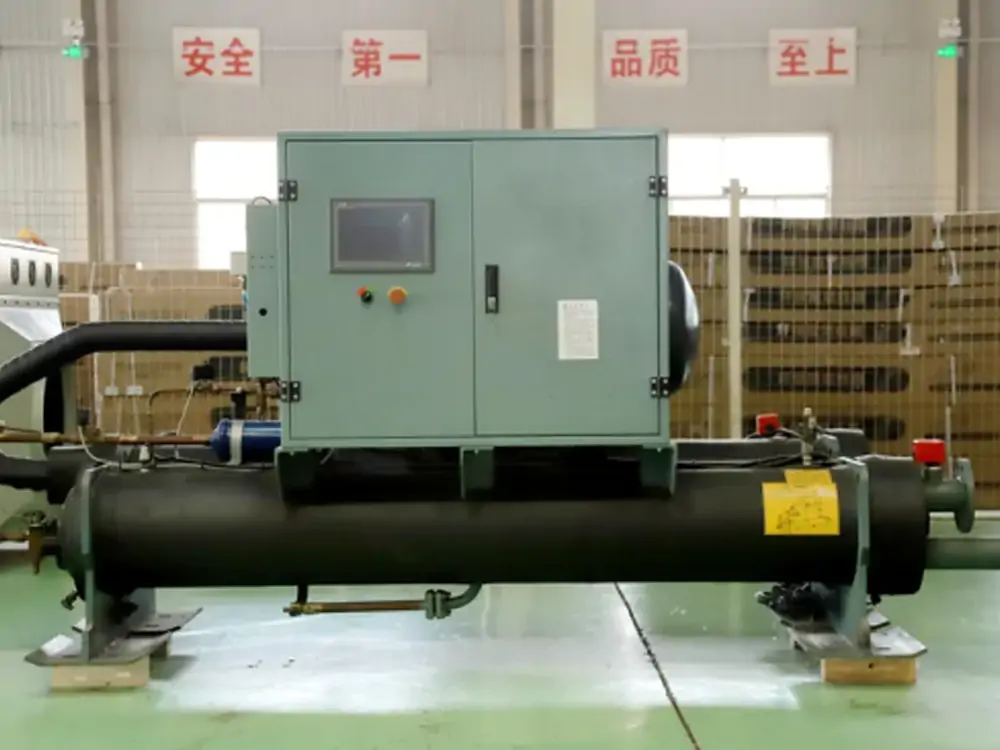
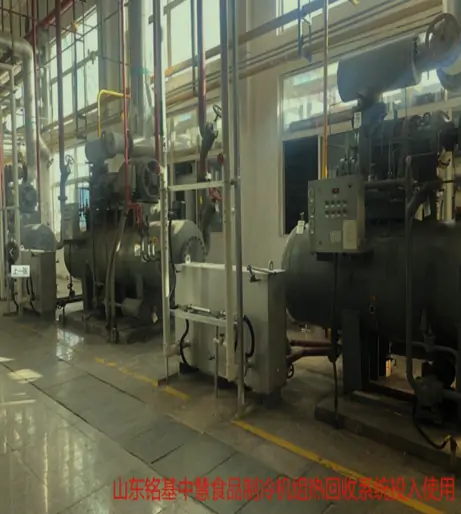
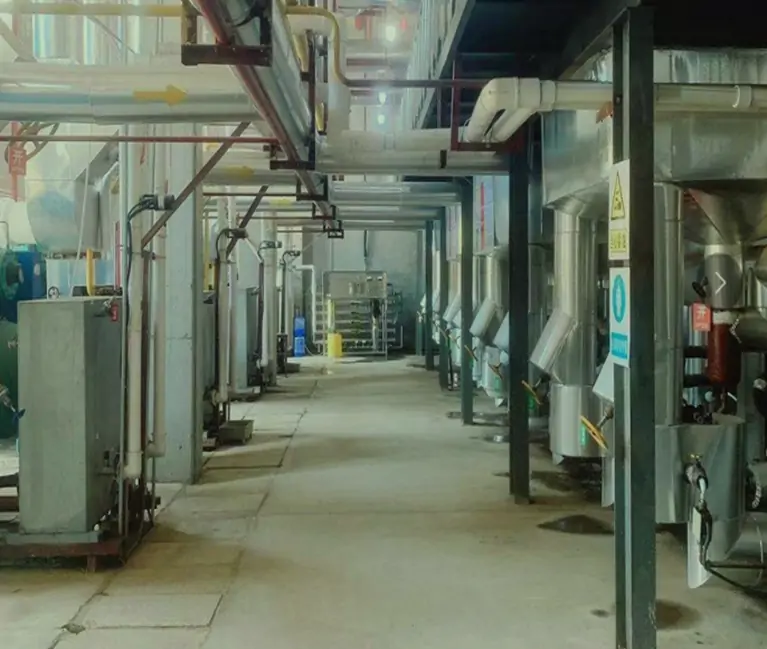
Civilian Water Cooling Unit Solution Systems, for residential/commercial use, have a pump, radiator/heat exchanger, and reservoir. The pump circulates water to absorb heat from a device/area like a computer CPU or server room. Heated water goes through the radiator to dissipate heat (assisted by a fan), and cooled water recirculates. This maintains proper temps, boosts equipment performance/lifespan, and operates quietly/efficiently.