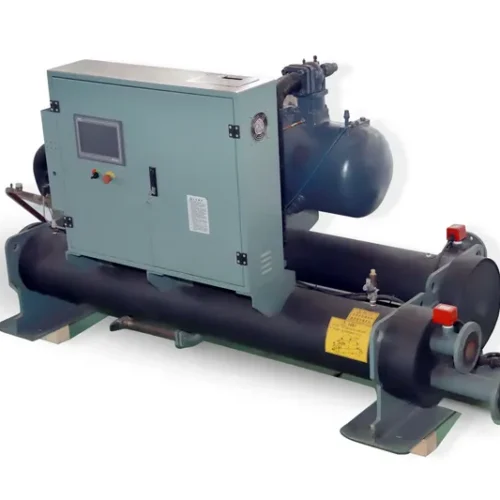
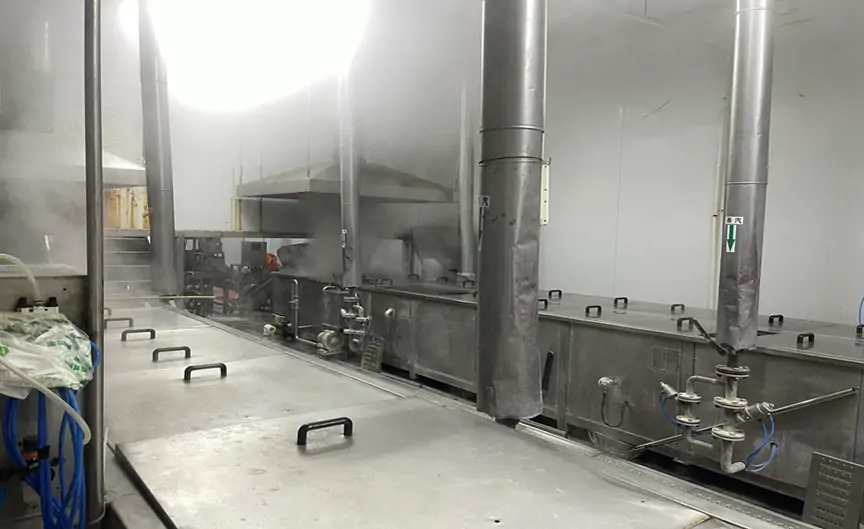
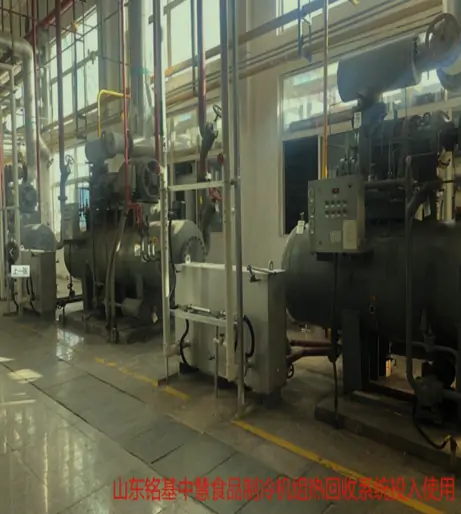
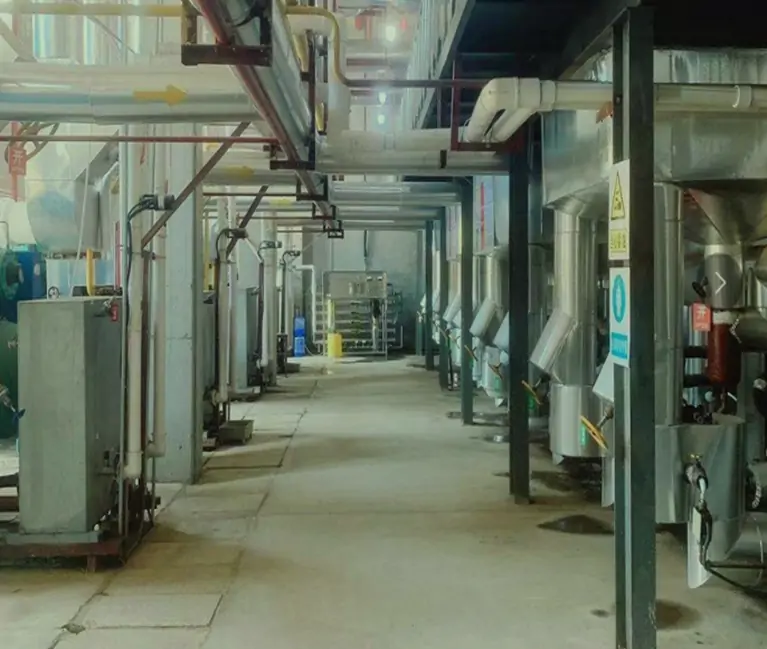
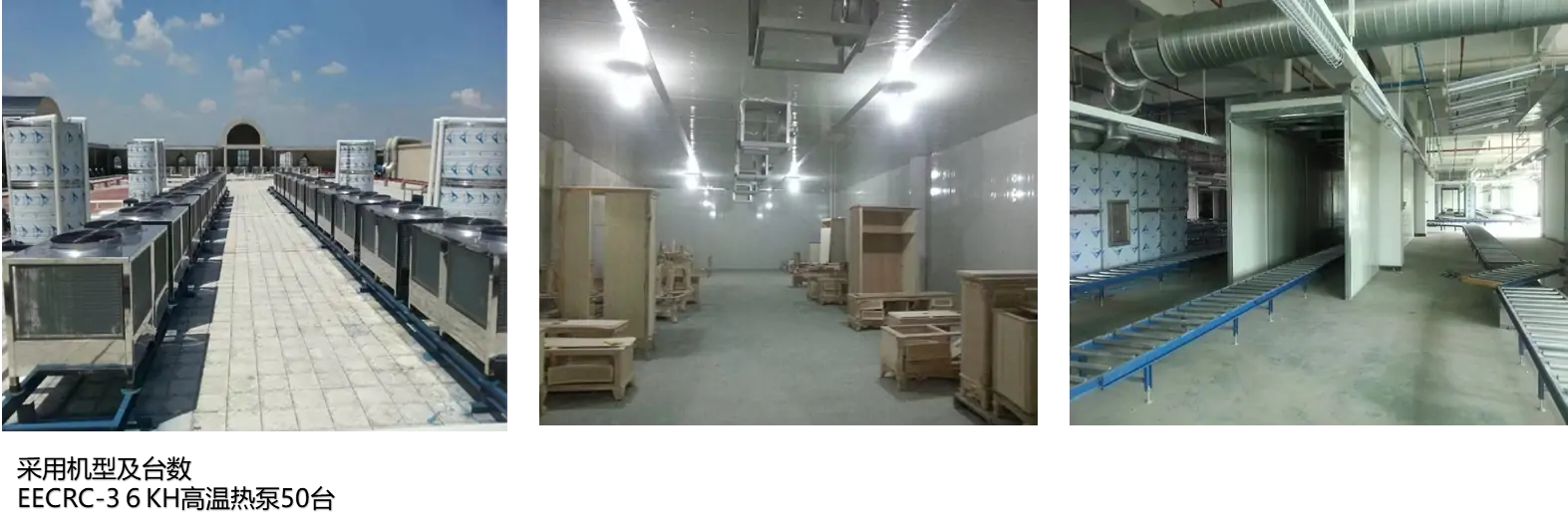
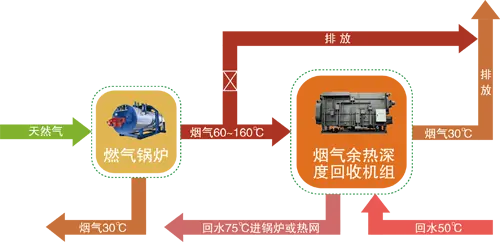
Waste heat recovery system/Industrial waste heat recovery solutions
The industrial waste heat recovery system uses advanced waste heat recovery technology to maximize the use of waste heat energy generated during the production process. The system intelligently controls and controls the industrial site to provide continuous and stable heat output regardless of external environmental conditions, improve production efficiency and reduce energy waste. The temperature difference fluctuation is controlled within ±0.5℃, providing an economical and efficient solution for your factory.
Energy-saving | Intelligent temperature control | Reduce carbon emissions | Improve production efficiency