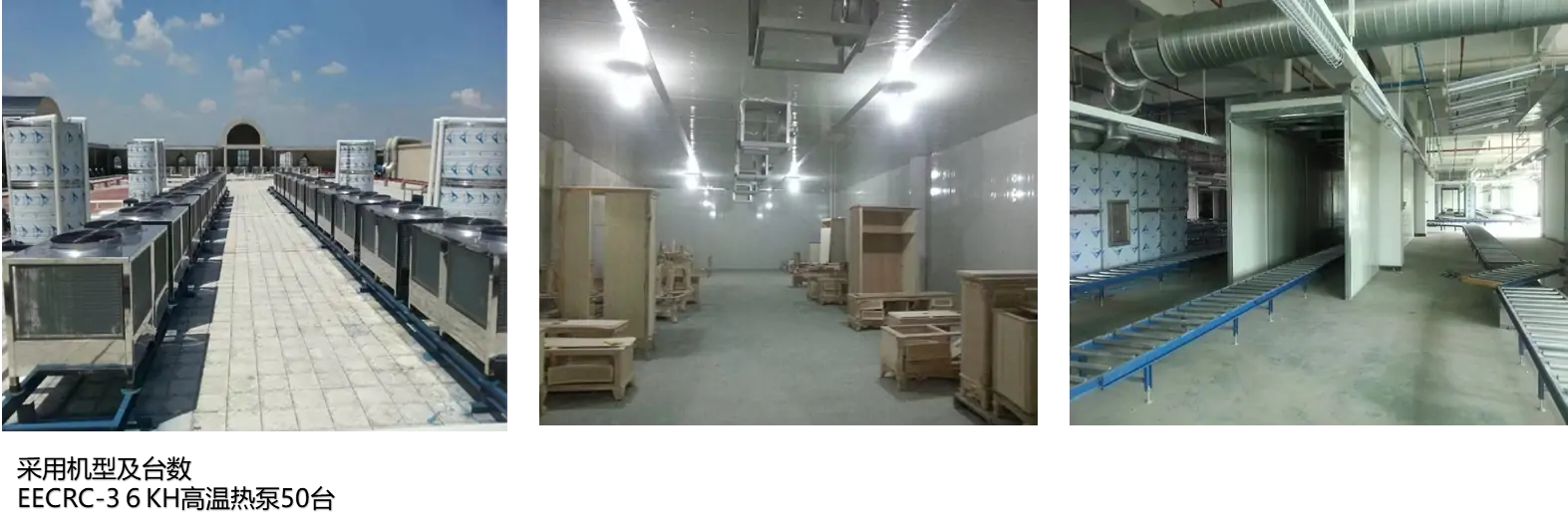
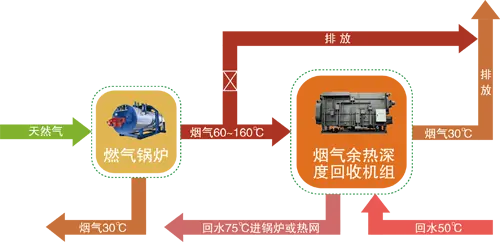
Industry Heat pump unit Solution systems
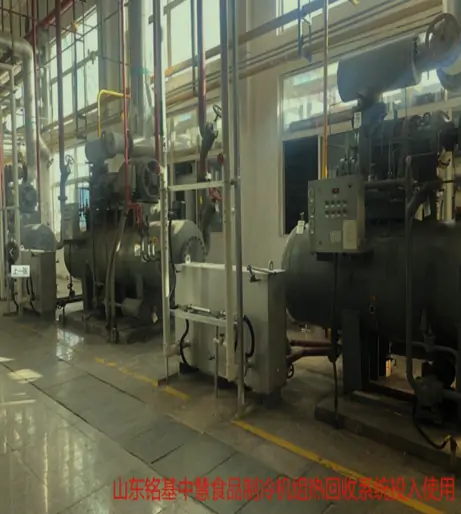
Industrial Heat Pump Unit Solution Systems for industrial use apply heat transfer. With compressor, heat exchangers, and refrigerant loop, they get heat from sources like air, water, or waste heat. In heating, upgrade and supply heat for processes. In cooling, absorb and dissipate heat. Energy-saving, cutting carbon footprints, and boosting efficiency and sustainability.