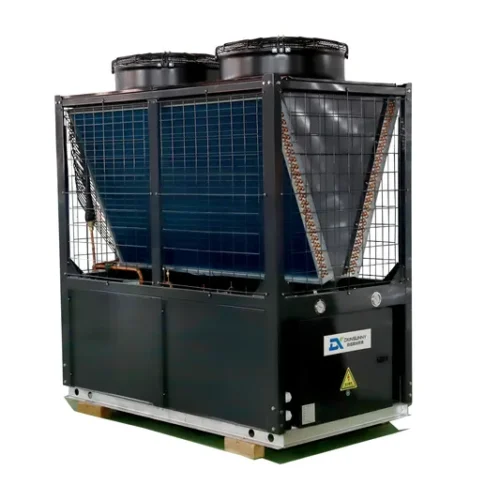
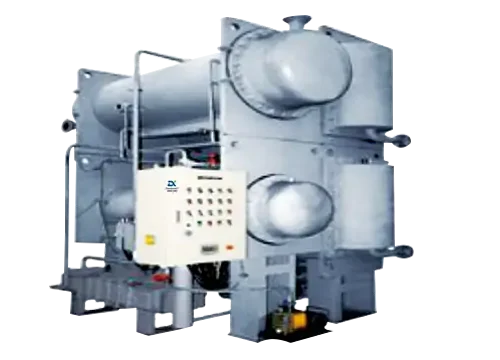
Core Advantages

Intelligent control system
- Precise temperature control: real-time monitoring of indoor and outdoor temperatures through intelligent sensors, automatically adjusting air conditioning output.
- Remote control function: supports mobile phone remote control to achieve intelligent management.
Efficient cooling and heating technology
- Frequency conversion technology: the central air conditioning system uses advanced frequency conversion compressors.
- Environmentally friendly refrigerants: use new environmentally friendly refrigerants to effectively reduce the impact on the environment.

Intelligent temperature control
High efficiency and energy saving

Remote mobile phone control

High efficiency and low noise

Dual frequency conversion function

Adaptive defrost effect
Intelligent temperature control
- Real-time monitoring of indoor and outdoor temperatures, automatic adjustment of cooling or heating mode, and always maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
- Divided area intelligent control, users can set different temperatures according to the needs of different rooms to improve overall energy efficiency.
High efficiency and energy saving
- Adopt advanced frequency conversion technology to reduce energy consumption, save operating costs, and ensure long-term use is more economical.
- Automatically adjust power output according to indoor temperature changes, reduce unnecessary power waste, and be environmentally friendly and energy-saving.
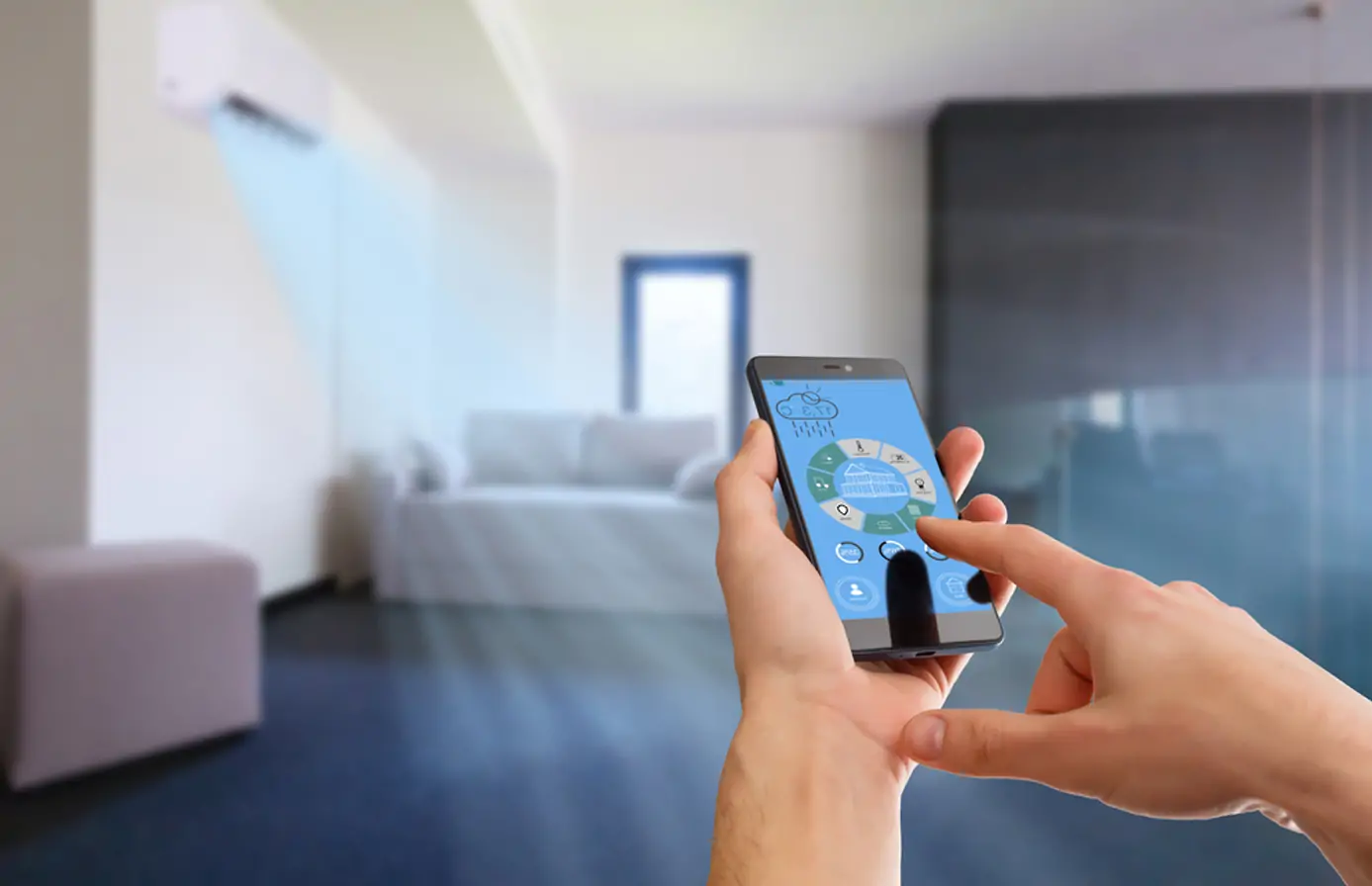


Remote mobile phone control
- Supports remote operation via mobile phone APP, allowing you to control the air conditioner switch and temperature adjustment anytime and anywhere, greatly improving convenience.
- You can remotely preset the working mode, adjust the room temperature in advance before arriving home, and enjoy a comfortable environment.
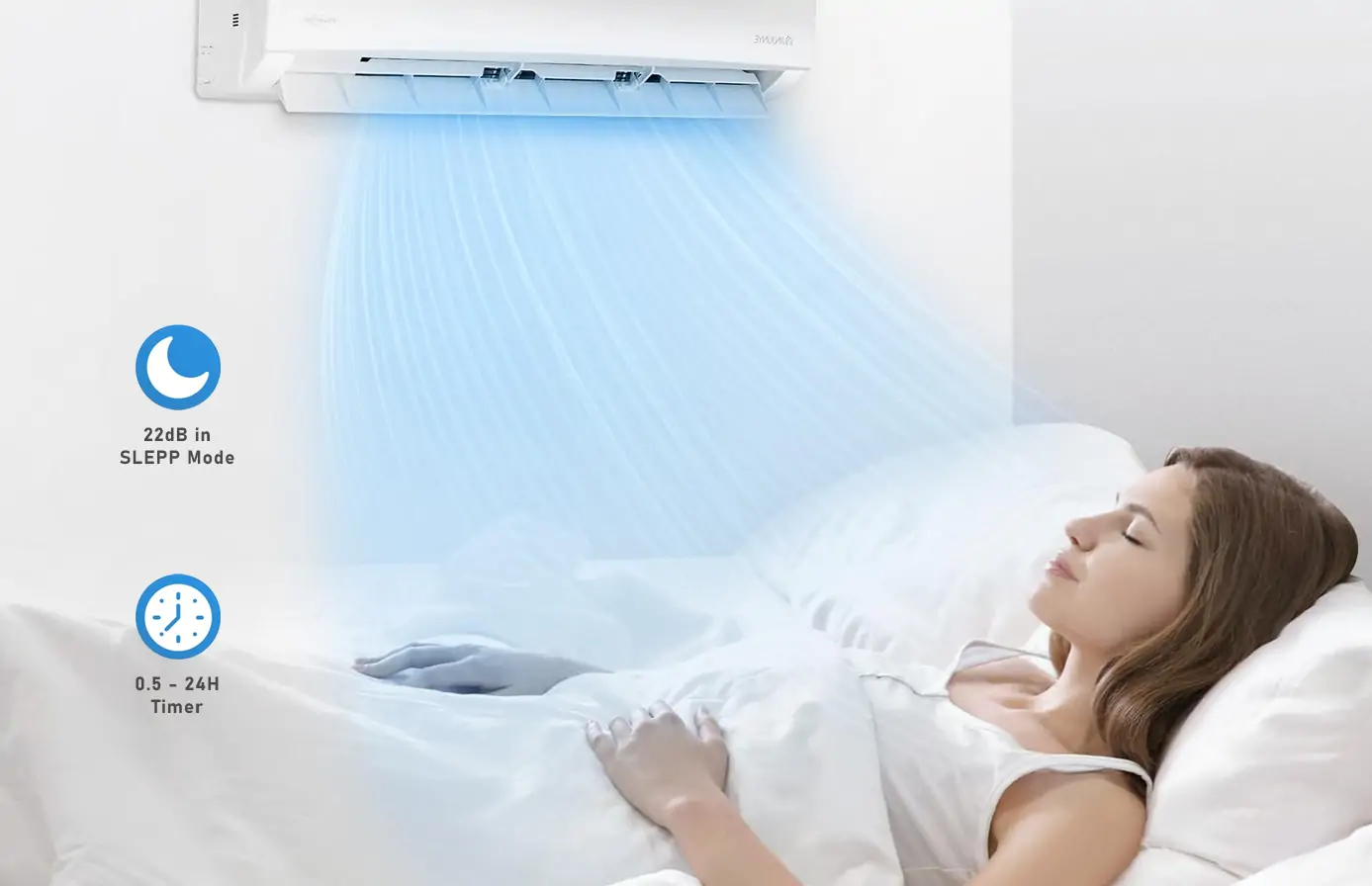
Efficient and low-noise operation
- Noise reduction technology is used to ensure that the device maintains a low noise state during operation, creating a quiet living and working environment for users.
- It maintains silent mode while operating efficiently, suitable for installation in bedrooms or office areas, without interfering with daily activities.
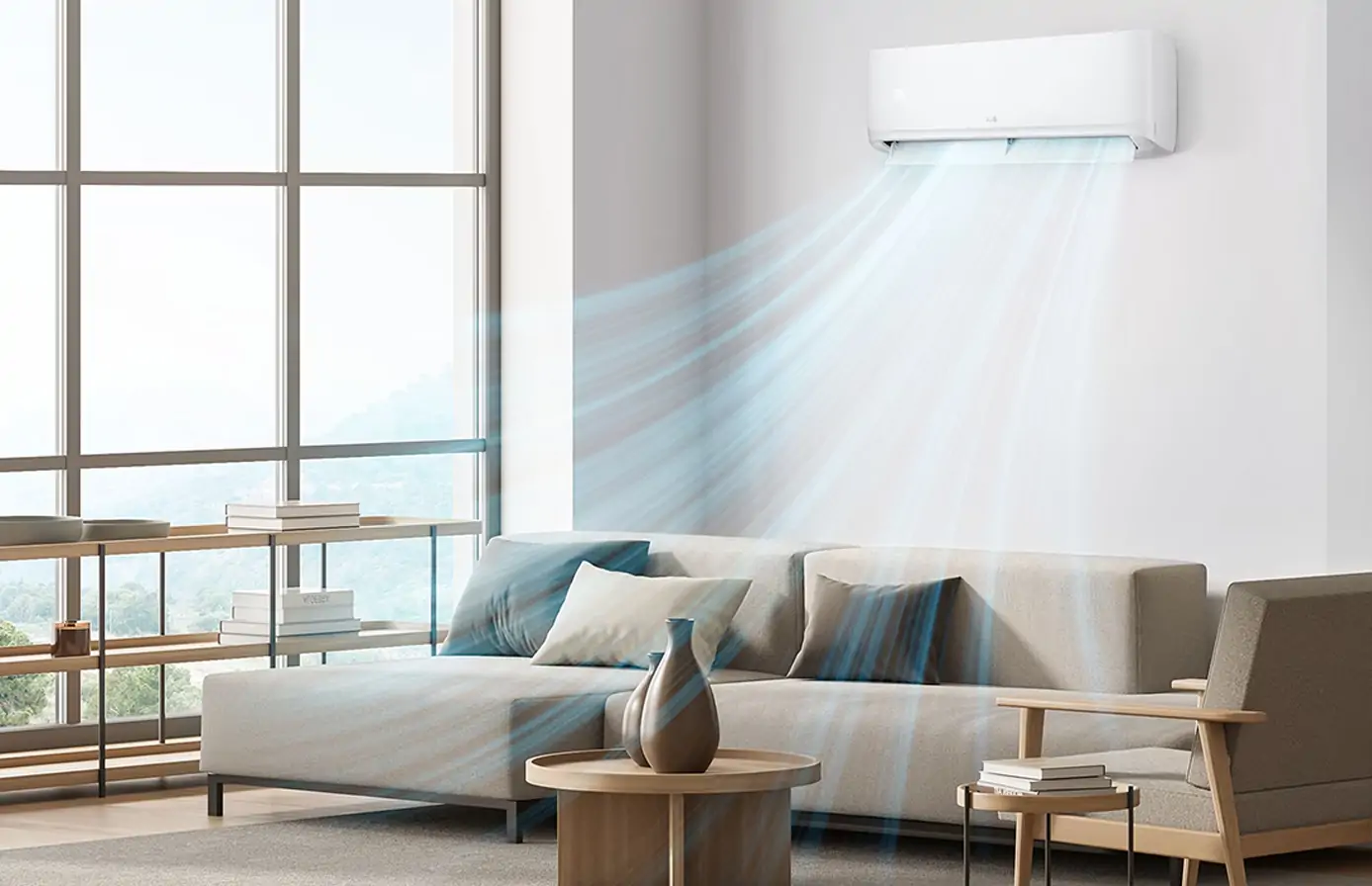


Dual frequency conversion technology
- Dual frequency conversion technology combines intelligent control of compressors and fans to provide fast cooling and heating effects, and more precise temperature regulation.
- Through intelligent frequency regulation, it reduces energy waste, extends equipment life, and improves system stability.
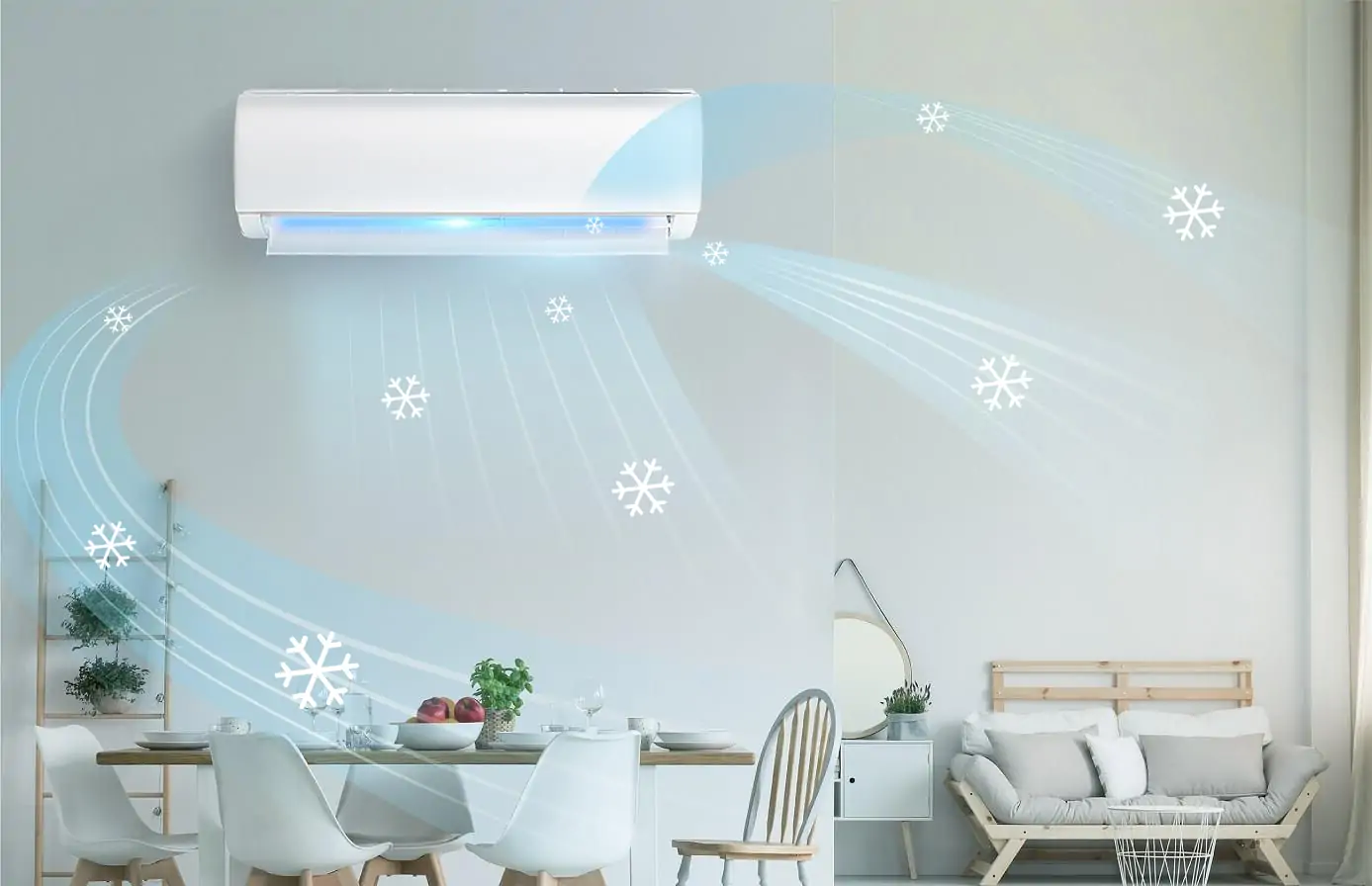
AI adaptive defrosting effect
- Intelligent adaptive defrosting technology can automatically start the defrosting function according to the external environment to ensure the normal operation of the air conditioner in a low temperature environment.
- Reduce the frequency of manual operation, automatically adjust the defrosting mode, avoid energy efficiency reduction caused by frost, and ensure the continuous and efficient operation of the system.

Product Specifications
| Product Specification | Details | Product Specification | Details |
| Heating Power | 6.0 kW | Energy Efficiency Rating | A++ |
| Refrigerant Type | R410A | Applicable Area | 50-150㎡ |
| Power Supply Voltage | 220V / 50Hz | Noise Level | ≤25 dB |
| Dual Inverter Technology | Supported | Smart Temperature Control | Supported |
| Remote Control | Mobile App Remote Control | Auto Defrost Function | Supported |
| Operating Temp Range | -15℃ to 45℃ | Weight | 40 kg |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 850mm x 300mm x 650mm | Installation Method | Ceiling / Wall Mounted |
Waste heat source heat pump unit Feature and Application:
Application:

Industrial Processes:
Utilizes waste heat from high-temperature processes like steel manufacturing, glass production, and chemical plants. Waste gases, steam, or other byproducts are converted into usable heat for heating or preheating water, space heating, or further industrial use.

Geothermal Energy:
Harnesses heat from geothermal tailwater or low-temperature geothermal resources, making Waste heat source heat pump unit ideal for heating buildings, greenhouses, or even for industrial heating.

District Heating and Cooling:
Captures waste heat from power plants, factories, or data centres to provide centralized heating or cooling for urban areas. Waste heat source heat pump unitreduces the need for traditional energy sources.

Wastewater Treatment Plants:
Extracts low-grade heat from sewage and wastewater for use in municipal or industrial heating, significantly improving energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
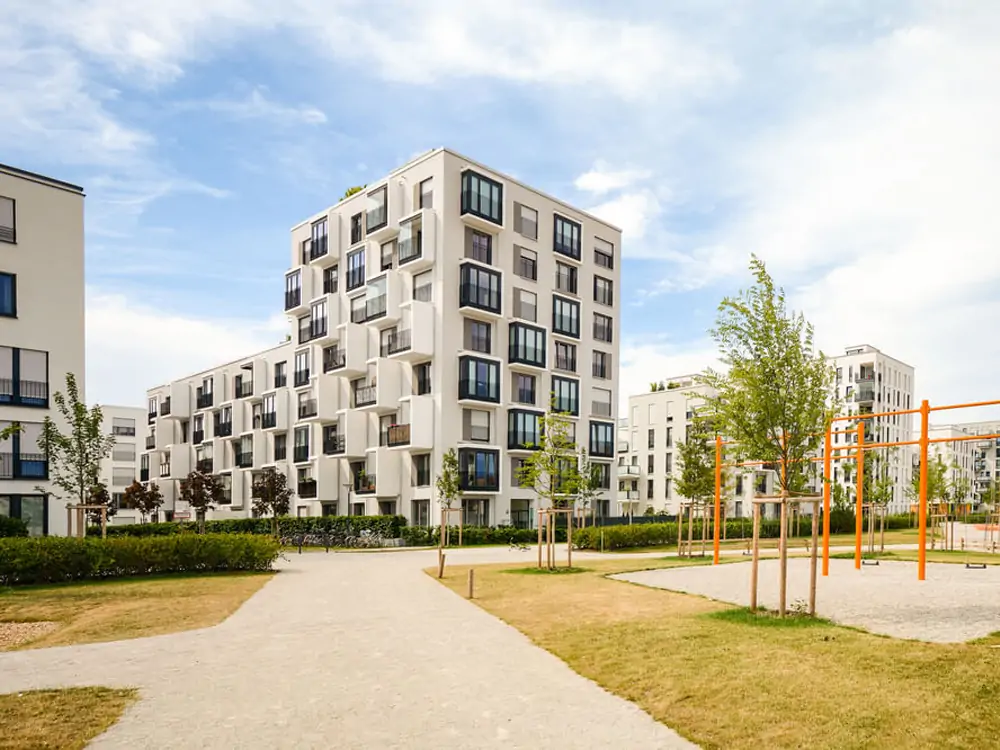

Commercial and Residential Buildings:
Waste heat source heat pump unit recovers heat from ventilation systems, refrigeration equipment, or exhaust gases in large buildings, shopping malls, and residential complexes, which can be used for heating or hot water supply.
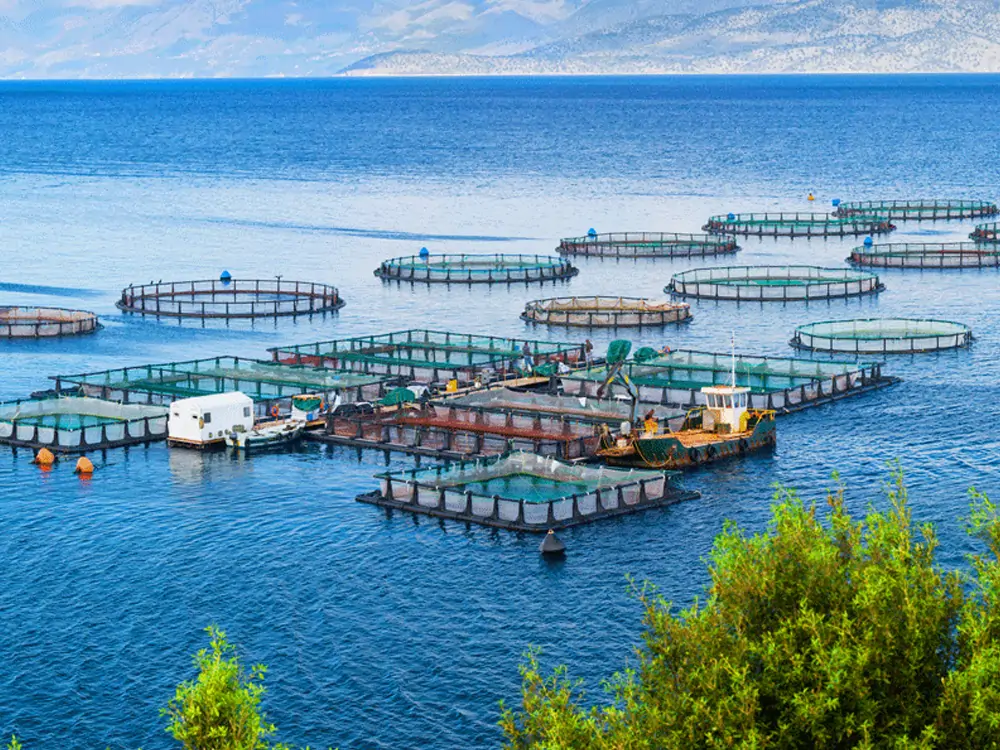

Agriculture and Aquaculture:
Can be used in greenhouses or fish farms to maintain optimal temperatures, improving productivity while reducing energy costs.
Waste heat source heat pump unit Details
Working Principle:
The waste heat source heat pump unit operates on the reverse Carnot cycle or vapor compression cycle. It takes low-temperature waste heat and upgrades it to a usable temperature using refrigerants and mechanical work. The basic steps include:
Heat Absorption:
Waste heat is absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator.
Compression:
The refrigerant is compressed in the compressor, raising its temperature and pressure.
Heat Release:
The heated refrigerant transfers its energy in the condenser to a secondary medium (such as water or air) for space heating, industrial processes, or hot water supply.
Expansion and Recycling:
The refrigerant expands and cools through the expansion valve, returning to its original state and repeating the process.


Efficiency and Performance:
The Coefficient of Performance (COP), a key measure of efficiency, typically ranges from 3 to 6, meaning for every unit of electricity consumed, the unit can produce 3 to 6 units of heat energy.
The system can efficiently upgrade low-grade heat (from as low as 10°C or 50°F) to usable temperatures (as high as 90°C or 195°F), depending on the application.
By recovering heat that would otherwise be wasted, the system significantly reduces energy consumption and operational costs.
Frequently asked questions
A Waste Heat Source Pump Unit is a device that captures and utilizes heat generated from industrial processes, machinery, or other waste heat sources to heat water, air, or other fluids. Instead of letting this heat escape as waste, the pump unit reuses it, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing overall energy costs.
The system captures low-grade waste heat and uses a heat pump to elevate its temperature to a usable level. The heat pump typically includes a compressor, evaporator, and condenser, allowing it to transfer and increase the temperature of the captured heat. The heated air, water, or fluid is then distributed as needed, often for space heating or other processes.
Waste heat source pump units can use a variety of waste heat sources, including:
- Exhaust from engines and turbines
- Industrial ovens and furnaces
- Refrigeration systems
- Air conditioning units
- Process waste heat from manufacturing and chemical industries
These units are commonly found in:
- Industrial facilities (factories, manufacturing plants)
- Power plants
- Commercial buildings
- Data centers
- Food processing facilities
- HVAC systems for large buildings
The energy savings depend on the quality and amount of waste heat available. A typical system can provide energy efficiency gains of 30-70% compared to traditional heating methods. In some cases, it can result in a significant reduction in heating costs.
- Availability of waste heat sources: Make sure there is sufficient and reliable waste heat.
- Heat quality: Assess the temperature and energy potential of the waste heat.
- System integration: Ensure the pump unit can be integrated into the existing heating or cooling system.
- Space and size constraints: Consider the physical space required for installation.
- Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate potential energy savings compared to the installation and maintenance costs.